In the world of textiles, viscose and rayon are key players. They are cellulosic materials that have greatly influenced fashion and textiles. They offer many benefits and characteristics, making them great choices for different uses. But what makes them different? Do they share more similarities than we think? Let’s explore the comparison between viscose and rayon, looking at their origins, properties, and environmental impact. Viscose vs Rayon
How do viscose and rayon differ in their chemical makeup, how they’re made, and their sustainability? Understanding these differences will help us appreciate these materials more. It will also show us the changing world of textile innovation and responsible sourcing.
Understanding Basic Textile Fibers: Natural and Synthetic Origins
The world of textiles is filled with different fibers, each with its own story. From the earth’s natural gifts to human innovation, the variety is vast. We’ll look at the main differences between natural and synthetic fibers, including where they come from, how they’re made, and how they’re classified.
Natural Fiber Sources and Processing
Natural fibers come straight from nature. They’re from plants, animals, or minerals. Examples include cotton, wool, silk, flax, and jute. Each fiber is carefully taken from its source, cleaned, and made ready for making textiles.
Cotton comes from cotton plants, while wool is sheared from sheep and other animals.
Synthetic Fiber Development and Manufacturing
Synthetic fibers, on the other hand, are made from chemicals. They use materials like petroleum, natural gas, or coal. You might know fabrics like polyester, nylon, and acrylic from this group.
These fibers are made to have specific qualities. This lets manufacturers create new and unique textiles to meet changing market needs.
Semi-synthetic Fiber Classification
Semi-synthetic or regenerated fibers fall between natural and synthetic. They include cellulosic materials like viscose and rayon. These fibers start from natural sources but are chemically altered to change their properties.
This group offers a mix of natural fiber’s sustainability and synthetic fiber’s versatility.
Knowing about these different fibers is key in the world of fabrics and textiles. Whether you’re in fashion, textile engineering, or just a consumer, this knowledge helps you make better choices. It also opens up the full potential of the textile industry.
| Fiber Type | Source | Processing |
| Natural Fibers | Plant-based (cotton, flax, jute) Animal-based (wool, silk) Mineral-based (asbestos) | Harvesting, cleaning, and preparation |
| Synthetic Fibers | Petroleum-based (polyester, nylon) Natural gas-based (acrylic) Coal-based (rayon) | Chemical processing and manufacturing |
| Semi-synthetic Fibers | Cellulosic materials (viscose, rayon) | Combination of natural and chemical processing |
“The textile industry is a tapestry of fibers, each with its own unique story, waiting to be woven into the fabric of our lives.”
The History and Evolution of Cellulosic Materials
The story of viscose fabric and rayon fabric is truly fascinating. It’s a journey through the history of textiles. These cellulosic materials have led the way in innovation, changing how we see and feel fabrics.
The start of viscose fabric goes back to the late 1800s. French chemist Hilaire de Chardonnet made the first artificial silk, called “Chardonnet silk.” This breakthrough led to the creation of viscose, a fiber made from plant cellulose.
In the early 1900s, British chemist Charles Frederick Cross and his team made a big leap. They developed the viscose process. This turned cellulose from wood pulp or plants into a fiber that felt like silk.
Soon after, rayon fabric emerged. Known as “artificial silk,” it was introduced in the early 1900s. It quickly became popular for its softness and ability to mimic natural fibers.
Over the years, making cellulosic materials has gotten better. Advances have been made in chemical processes, fiber creation, and making it more eco-friendly. Today, viscose fabric and rayon fabric are key in the textile world. They offer a wide range of uses and flexibility for fashion, home decor, and more.
| Year | Milestone |
| 1884 | Hilaire de Chardonnet develops the first artificial silk, known as “Chardonnet silk”. |
| 1905 | Charles Frederick Cross and colleagues develop the viscose process for producing regenerated cellulose fiber. |
| 1910 | Rayon, also known as “artificial silk,” is introduced to the textile market. |
| Present Day | Ongoing advancements in cellulosic material production, including improved sustainability and environmental impact. |
“The development of cellulosic materials has been a transformative journey, reshaping the textile industry and the way we experience fabrics.”
Viscose vs Rayon: A Comprehensive Comparison
Viscose and rayon are often confused with each other. But they are different in many ways. Knowing the differences helps us choose better for our clothes and the planet.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Both viscose and rayon come from cellulose, found in plants. But they are made differently. Viscose uses chemicals like carbon disulfide to create its fibers. Rayon, however, has many types, each made in a unique way.
Manufacturing Processes
How viscose and rayon are made is quite different. Viscose goes through many steps to become a fiber. Rayon, on the other hand, can be made in several ways, each with its own effects on the environment.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
The way viscose and rayon are made affects the planet. Viscose uses a lot of water and can harm the environment. Rayon, especially the lyocell method, is better for the planet.
“The choice between viscose and rayon is not merely a matter of aesthetics, but a decision that can have a significant impact on the environment and our collective commitment to sustainability.”
Knowing the differences helps us choose better. This way, we can support sustainable fashion and care for our planet.
Physical Properties and Performance Characteristics
Viscose and rayon fabrics have unique physical properties and performance. They are known for being breathable and moisture-wicking. This makes them great for many textile uses.
Breathability is key, as it lets air flow freely. This keeps the wearer cool and comfy. Viscose and rayon are top-notch in this area, thanks to their porous structure. They’re perfect for summer clothes and activewear.
Moisture-wicking is another strong point. These fibers pull moisture away from the skin. They help keep you dry and comfy, even when you’re active. This is why they’re popular in sportswear and performance fabrics.
Durability can vary with viscose and rayon. They’re not as durable as some natural fibers like cotton or linen. But, better manufacturing methods have made them stronger. With the right care, they can last a good while.
| Property | Viscose | Rayon |
| Breathability | Excellent | Excellent |
| Moisture-wicking | Excellent | Excellent |
| Durability | Moderate | Moderate to High |
Viscose and rayon are versatile and appealing for many uses. Their breathability and moisture-wicking, along with manufacturing improvements, keep them in demand.
Manufacturing Process: From Wood Pulp to Fabric
The journey from wood pulp to fabric is fascinating. It involves several steps. At the core are the techniques for making viscose and rayon. These are key materials in the textile world.
Raw Material Selection
The first step is picking the right raw materials. Viscose and rayon come from wood pulp. This pulp comes from forests managed for sustainability.
The pulp then goes through chemical and mechanical processes. These steps extract the cellulose, the main part of these fabrics.
Chemical Treatment Steps
Next, the cellulose gets a series of chemical treatments. It’s dissolved, filtered, and stabilized to make a viscose solution. This solution is pushed through tiny holes, making fine filaments.
These filaments are then processed into yarn or fabric. The type of fabric depends on the desired look and feel.
Fiber Formation and Processing
The last step is forming and processing the fibers. The filaments are woven or knitted into fabric. This step considers the fabric’s weight, texture, and how it performs.
This journey shows the textile industry’s commitment to sustainability. It aims to make innovative, eco-friendly fashion for today’s shoppers.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The demand for sustainable fashion and eco-friendly fabrics is rising. This has made people look closely at the environmental impact of viscose and rayon. These materials are popular for their feel and look but can harm the environment if not made carefully.
Viscose and rayon use natural resources like wood pulp and chemicals in making. This can cause worries about using up resources, polluting water, and releasing harmful gases.
Addressing Sustainability Challenges
The textile industry is working hard to lessen the harm caused by viscose and rayon. They are trying new ways and following green practices. Some of these efforts include:
- Getting wood pulp from forests that are managed well
- Using systems that close loops to cut down waste and chemicals
- Using green energy to power factories
- Creating fibers from bamboo and other plant waste
Big names in sustainable fashion are teaming up with green groups. They set and follow strict rules to make sure their products are good for the planet.
| Sustainability Metric | Viscose | Rayon |
| Water Consumption (liters/kg) | 100-150 | 75-100 |
| Energy Consumption (kWh/kg) | 12-18 | 10-15 |
| Carbon Footprint (kg CO2e/kg) | 2.5-3.5 | 2.0-2.8 |
The textile world is moving towards a greener future with viscose and rayon. They are using new methods and green practices. This is helping to make fashion more eco-friendly.
“The future of fashion lies in its ability to be both stylish and environmentally responsible. By embracing sustainable materials like viscose and rayon, we can create a greener, more sustainable industry.”
Applications in Fashion and Textile Industry
Viscose and rayon fabrics are key in the fashion and textile world. They are used in many ways, from clothes to home items and industrial uses.
Clothing and Apparel Uses
These fabrics are popular in clothes because they are soft and breathable. They are great for blouses, dresses, and even men’s shirts. They also work well for activewear because they wick away moisture.
Home Textile Applications
Viscose and rayon are also big in home textiles. They make bedding like sheets and duvet covers feel luxurious. They’re also used in curtains and upholstery, adding elegance to homes.
Industrial Applications
Viscose and rayon go beyond fashion and home use. They’re used in filters, insulation, and as strong fibers in composites. Their durability makes them valuable in industry.
| Application | Viscose Fabric | Rayon Fabric |
| Clothing and Apparel | Blouses, dresses, skirts, activewear | Men’s shirts, women’s tops, sportswear |
| Home Textiles | Bedding, curtains, upholstery | Sheets, duvet covers, pillowcases |
| Industrial | Filters, insulation, composite materials | Reinforcing fibers, industrial applications |
Viscose and rayon’s wide use shows their big role in fashion and textiles. They meet the changing needs of both consumers and industries.
Care Instructions and Maintenance Tips
Caring for viscose and rayon fabrics needs a gentle touch. This keeps them soft, smooth, and colorful. These materials, made from cellulose, need special care to last and look great. Here are the key tips to keep your viscose and rayon items in top shape.
Washing and Drying
When washing, use cold water and a mild detergent. Hot water can shrink or distort the fabric. Dry on a low setting or air dry to avoid too much heat.
Ironing and Storage
Ironing should be done with care. Use low heat and a pressing cloth to avoid damage. Store items by hanging or folding them carefully to prevent wrinkles.
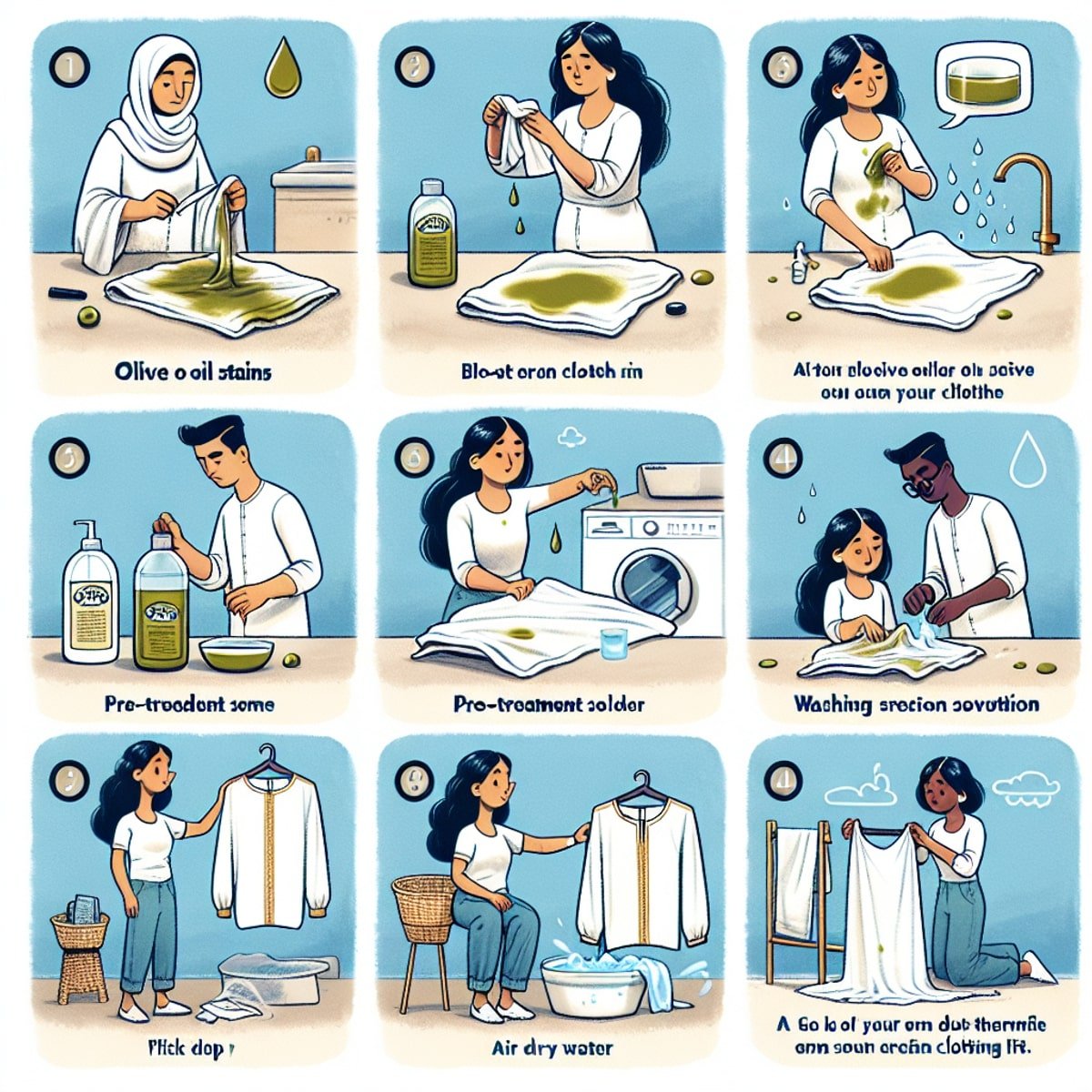
Stain Removal
- Blot stains with a clean, damp cloth right away.
- Don’t rub or scrub to avoid damaging the fabric.
- For stubborn stains, use a mild stain remover. Test it first on a small area.
By following these care tips, you can keep your viscose and rayon fabrics looking and feeling great. They will remain comfortable, breathable, and elegant for a long time.
“Proper care is the key to making the most of your viscose and rayon investments.”
Conclusion
We’ve looked closely at the differences between viscose and rayon. These two materials are similar but have unique qualities. We’ve learned about their makeup, how they’re made, and their impact on the environment.
The need for green fashion is growing, and viscose and rayon are key players. New ways to make them are being explored. This means they could help make the fashion world more eco-friendly.
Choosing the right fabrics is important for a greener fashion world. By understanding viscose and rayon, we can make better choices. This helps us all move towards a more sustainable future.
The debate over viscose and rayon shows how fast the textile world is changing. It’s important to keep up with these changes. This way, we can support the shift towards more sustainable fashion.
FAQ
Q: What is the difference between viscose and rayon?
A: Viscose and rayon are both made from natural materials. They differ in their chemical makeup, how they’re made, and their impact on the environment.
Q: What are the main sources for viscose and rayon?
A: Viscose usually comes from wood pulp or bamboo. Rayon can come from wood, bamboo, or even recycled cotton.
Q: How are viscose and rayon manufactured?
A: Viscose is made by dissolving cellulose in a special solution. Rayon’s production varies, depending on the type being made.
Q: What are the environmental impacts of viscose and rayon production?
A: Making both viscose and rayon can harm the environment. This includes pollution, emissions, and the use of harmful chemicals. But, new, greener ways to make them are being developed.
Q: How do the physical properties of viscose and rayon compare?
A: Viscose and rayon are similar in many ways. They are light, breathable, and good at wicking moisture. But, their exact properties can change based on how they’re made and used.
Q: What are the common applications of viscose and rayon fabrics?
A: These fabrics are used in many things. This includes clothes, home textiles, and even some medical items.
Q: How should viscose and rayon fabrics be cared for?
A: To keep these fabrics looking good, wash them gently and dry them on low heat. Always follow the care instructions from the maker to keep them in top shape.